Distribution system
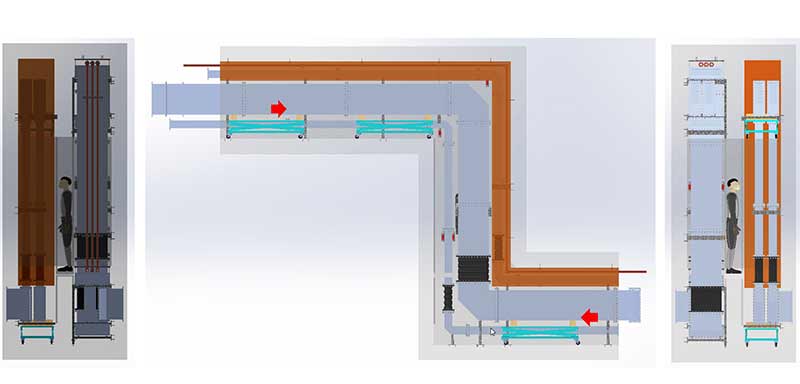
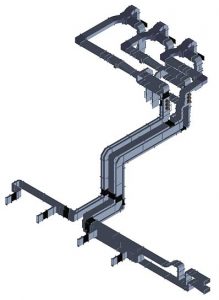
RF distribution networks carry the RF power from the am- plifiers in the RF gallery up to the accelerating cavities in- side the tunnel, which are located some 40 meters apart. RFQ and DTL RF power stations use large rectangular wa- veguides (roughly 60 cm wide hollow tubes).
Not only straight sections and bends are needed, but also flexible sections, power splitters, phase shifters, directio- nal couplers, shutter switches, adapters and mechanical supports. The waveguide layout was routed by ESS ERIC and ESS Bilbao, to connect the RF power sources and the cavities, while guaranteeing exact phase matching between each pair of couplers. Then, most of the waveguide com- ponents have been developed, produced, and delivered by Spanish companies such as Rymsa RF-Sener Aerospacial and AWGE Technologies S.L., as well as the American com- pany Mega Industries.
On the other hand, the construction of high-power circula- tors and loads was awarded to AFT Microwave GmbH.
The main challenge related to the design of waveguide components is the high electric field which can cause ar- cing and eventually damage on the surfaces. So, provisions of arc detection were also installed to quickly turn off RF in case of arcs.

The distribution system consists of the following main part:
This system includes different components with a specific function:
- Circulator: protect the amplifiers from RF power reflection from the cavity.
- High power load: dissipates the backscattered power.
- Magic Tee: splits the RF high power in two paths.
- Dual Directional coupler: monitories the forward and reflected power for safety purposes.
- Phase shifter: compensates the phase differences between divided paths.
- Arc sensor: detects arc during conditioning and operation.
Distribution-system
WR2300 components
WR2300 component
Stub layouts
The stubs are the narrow ducts going down to the tunnel from the gallery. These ducts will house all cooling water pipes and all cables needed for tunnel components.
Due to the space constraints, ESS Bilbao is developing the correct installation sequence of all components for the two stubs of the normal conducting linac: